반응형
다중 선형 회귀
입력값이 많다면 그에 맞게 경사하강법을 사용해야한다.
$y = a_1x_1 + a_2x_2 + b$에 대한 평균 제곱 오차를 $a_1, a_2, b$에 대해서 편미분해야한다.
${1 \over n}\sum(y_i-(a_1x_1 + a_2x_2 + b))^2$을 $a_1, a_2, b$로 편미분하면
${2 \over n}\sum(y_i-(a_1x_1 + a_2x_2 + b))(-x_1) = -{1 \over n}\sum((error)_(x_1))$
${2 \over n}\sum(y_i-(a_1x_1 + a_2x_2 + b))(-x_2) = -{1 \over n}\sum((error)*(x_2))$
${2 \over n}\sum(y_i-(a_1x_1 + a_2x_2 + b))(-1) = -{1 \over n}\sum(error)$
미리보는 모르는 함수
matplotlib.pyplot.axes(arg=None, \*\*kwargs)
plt.axes(rect, projection=None, polar=False, \*\*kwargs)기본적으론 이런 형태로 선언된다.
projection='3d'로하면 3차원 그래프가 반환된다.
이와 연계하여
Axes.scatter(self, x, y, s=None, c=None, marker=None, cmap=None, norm=None, vmin=None, vmax=None, alpha=None, linewidths=None, *, edgecolors=None, plotnonfinite=False, data=None, **kwargs)
함수도 있다... 근데 대체 저 레퍼런스의 어딜봐서 한 점에 관한 값이 axes개수만큼 들어갈 수 있다는 건지 모르겠다. 참...
실제 코드
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits import mplot3d
#공부시간 X와 성적 Y의 리스트를 만듭니다.
data = [[2, 0, 81], [4, 4, 93], [6, 2, 91], [8, 3, 97]]
x1 = [i[0] for i in data]
x2 = [i[1] for i in data]
y = [i[2] for i in data]
#그래프로 확인해 봅니다.
#3D 그래프는 pyplot.axes를 사용하여 표시한다.
ax = plt.axes(projection='3d')
ax.set_xlabel('study_hours')
ax.set_ylabel('private_class')
ax.set_zlabel('Score')
ax.dist = 11
ax.scatter(x1, x2, y)
plt.show()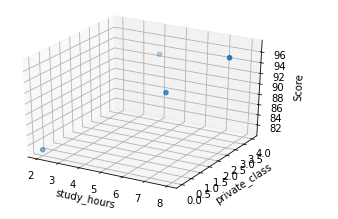
#리스트로 되어 있는 x와 y값을 넘파이 배열로 바꾸어 줍니다.(인덱스를 주어 하나씩 불러와 계산이 가능해 지도록 하기 위함입니다.)
x1_data = np.array(x1)
x2_data = np.array(x2)
y_data = np.array(y)
# 기울기 a와 절편 b의 값을 초기화 합니다.
a1 = 0
a2 = 0
b = 0
#학습률을 정합니다.
lr = 0.05
#몇 번 반복될지를 설정합니다.(0부터 세므로 원하는 반복 횟수에 +1을 해 주어야 합니다.)
epochs = 2001
#경사 하강법을 시작합니다.
for i in range(epochs): # epoch 수 만큼 반복
y_pred = a1 * x1_data + a2 * x2_data + b #y를 구하는 식을 세웁니다
error = y_data - y_pred #오차를 구하는 식입니다.
a1_diff = -(1/len(x1_data)) * sum(x1_data * (error)) # 오차함수를 a1로 미분한 값입니다.
a2_diff = -(1/len(x2_data)) * sum(x2_data * (error)) # 오차함수를 a2로 미분한 값입니다.
b_new = -(1/len(x1_data)) * sum(y_data - y_pred) # 오차함수를 b로 미분한 값입니다.
a1 = a1 - lr * a1_diff # 학습률을 곱해 기존의 a1값을 업데이트합니다.
a2 = a2 - lr * a2_diff # 학습률을 곱해 기존의 a2값을 업데이트합니다.
b = b - lr * b_new # 학습률을 곱해 기존의 b값을 업데이트합니다.
if i % 100 == 0: # 100번 반복될 때마다 현재의 a1, a2, b값을 출력합니다.
print("epoch=%.f, 기울기1=%.04f, 기울기2=%.04f, 절편=%.04f" % (i, a1, a2, b))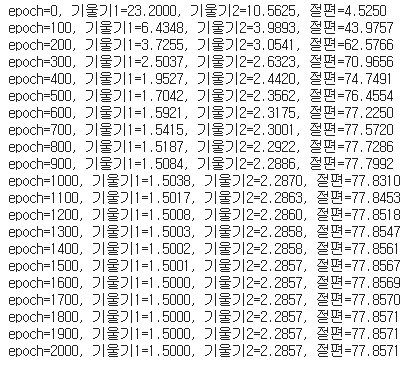
#참고 자료, 다중 선형회귀 '예측 평면' 3D로 보기
import statsmodels.api as statm
import statsmodels.formula.api as statfa
from matplotlib.pyplot import figure
X = [i[0:2] for i in data] # attribute
y = [i[2] for i in data] # class
X_1=statm.add_constant(X)
results=statm.OLS(y,X_1).fit()
hour_class=pd.DataFrame(X,columns=['study_hours','private_class'])
hour_class['Score']=pd.Series(y)
model = statfa.ols(formula='Score ~ study_hours + private_class', data=hour_class)
results_formula = model.fit()
a, b = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(hour_class.study_hours.min(),hour_class.study_hours.max(),100),
np.linspace(hour_class.private_class.min(),hour_class.private_class.max(),100))
X_ax = pd.DataFrame({'study_hours': a.ravel(), 'private_class': b.ravel()})
fittedY=results_formula.predict(exog=X_ax)
fig = plt.figure()
graph = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
graph.scatter(hour_class['study_hours'],hour_class['private_class'],hour_class['Score'],
c='blue',marker='o', alpha=1)
graph.plot_surface(a,b,fittedY.values.reshape(a.shape),
rstride=1, cstride=1, color='none', alpha=0.4)
graph.set_xlabel('study hours')
graph.set_ylabel('private class')
graph.set_zlabel('Score')
graph.dist = 11
plt.show()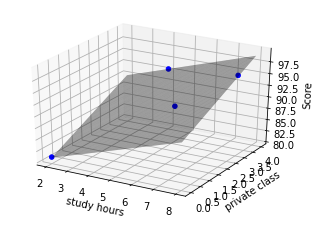
_
반응형
'AI > 모두의 딥러닝' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Deep Learning : 딥러닝] 오차 역전파와 XOR 문제 (0) | 2021.06.09 |
|---|---|
| [Deep Learning : 딥러닝] 퍼셉트론과 XOR 문제 (0) | 2021.06.09 |
| [Deep Learning : 딥러닝] 로지스틱 회귀(Logistic Regression) (0) | 2021.05.16 |
| [Deep Learning : 딥러닝] 경사하강법, 선형 회귀(Gradient descent, Linear Regression) (0) | 2021.05.15 |
| 딥러닝 입문 - 최소제곱법, 평균제곱오차, 딥러닝의 기본 연산(method of least squares, Mean squared error) (2) | 2021.05.08 |